Configurations for Single Root I/O Virtualization
SR-IOV (Single Root I/O Virtualization) is a hardware feature that allows a single physical device to be recognized by a hypervisor as if it were multiple separate devices. For example, a machine with a single NIC that supports SR-IOV can be recognized as if it has multiple NICs by using SR-IOV, and each NIC can be passed through to the VM.
This page contains some notes on using SR-IOV with KVM.
System Setup
- Hardware
- CPU: Intel Core-i9 9900K
- NIC: Intel Corporation I350 Gigabit Network Connection
- Motherboard: PRIME H310M-AT R2.0
- OS
- Host: Arch
- Guest
- VM1: ubuntu 20.04 server
- VM2: ubuntu 20.04 server
Configurations for BIOS
Enable VT-d in the BIOS.
Enable SR-IOV
Create a configuration file /etc/modprobe.d/igb.conf for modprobe.
sudo vim /etc/modprobe.d/igb.conf
options igb max_vfs=4
#blacklist igbvf
Grub
To enable IOMMU, change the Grub configuration and add kernel options.
sudo vim /etc/default/grub
-GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX_DEFAULT="loglevel=3 quiet"
+GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX_DEFAULT="loglevel=3 quiet intel_iommu=on iommu=pt"
sudo grub-mkconfig -o /boot/grub/grub.cfg
reboot
When the Error Occurs
Here is what to do if you get an error in dmesg.
sudo dmesg | grep igb
[ 2.070715] igb: Intel(R) Gigabit Ethernet Network Driver
[ 2.070717] igb: Copyright (c) 2007-2014 Intel Corporation.
[ 2.126386] igb 0000:01:00.0: added PHC on eth0
[ 2.126389] igb 0000:01:00.0: Intel(R) Gigabit Ethernet Network Connection
[ 2.126389] igb 0000:01:00.0: eth0: (PCIe:5.0Gb/s:Width x4) 80:61:5f:05:e2:ec
[ 2.126465] igb 0000:01:00.0: eth0: PBA No: 106300-000
[ 2.126465] igb 0000:01:00.0: Using MSI-X interrupts. 8 rx queue(s), 8 tx queue(s)
[ 2.180163] igb 0000:01:00.1: added PHC on eth1
[ 2.180164] igb 0000:01:00.1: Intel(R) Gigabit Ethernet Network Connection
[ 2.180165] igb 0000:01:00.1: eth1: (PCIe:5.0Gb/s:Width x4) 80:61:5f:05:e2:ed
[ 2.180238] igb 0000:01:00.1: eth1: PBA No: 106300-000
[ 2.180239] igb 0000:01:00.1: Using MSI-X interrupts. 8 rx queue(s), 8 tx queue(s)
[ 2.274584] igb 0000:01:00.0 enp1s0f0: renamed from eth0
[ 2.317450] igb 0000:01:00.1 enp1s0f1: renamed from eth1
[ 5.510141] igb 0000:01:00.0 enp1s0f0: igb: enp1s0f0 NIC Link is Up 1000 Mbps Full Duplex, Flow Control: RX/TX
[ 6.363591] igb 0000:01:00.1 enp1s0f1: igb: enp1s0f1 NIC Link is Up 1000 Mbps Full Duplex, Flow Control: RX/TX
[ 643.338345] igb 0000:01:00.0: can't enable 2 VFs (bus 02 out of range of [bus 01])
[ 687.182846] igb 0000:01:00.0: can't enable 2 VFs (bus 02 out of range of [bus 01])
[ 705.005251] igb 0000:01:00.0: can't enable 1 VFs (bus 02 out of range of [bus 01])
Add the following options to the kernel options in grub configuration.
-GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX_DEFAULT="loglevel=3 quiet intel_iommu=on iommu=pt"
+GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX_DEFAULT="loglevel=3 quiet intel_iommu=on iommu=pt pci=assign-busses"
pci=assign-busses: Make the kernel always assign all PCI bus numbers
Create grub config file and reboot.
sudo grub-mkconfig -o /boot/grub/grub.cfg
reboot
Check iommu_group
find /sys/kernel/iommu_groups/ -type l
Check support for ACS (Access Control Services)
The following is the list of PCI devices.
lspci | grep Ethernet
01:00.0 Ethernet controller: Intel Corporation I350 Gigabit Network Connection (rev 01)
01:00.1 Ethernet controller: Intel Corporation I350 Gigabit Network Connection (rev 01)
02:10.0 Ethernet controller: Intel Corporation I350 Ethernet Controller Virtual Function (rev 01)
02:10.1 Ethernet controller: Intel Corporation I350 Ethernet Controller Virtual Function (rev 01)
02:10.4 Ethernet controller: Intel Corporation I350 Ethernet Controller Virtual Function (rev 01)
02:10.5 Ethernet controller: Intel Corporation I350 Ethernet Controller Virtual Function (rev 01)
02:11.0 Ethernet controller: Intel Corporation I350 Ethernet Controller Virtual Function (rev 01)
02:11.1 Ethernet controller: Intel Corporation I350 Ethernet Controller Virtual Function (rev 01)
02:11.4 Ethernet controller: Intel Corporation I350 Ethernet Controller Virtual Function (rev 01)
02:11.5 Ethernet controller: Intel Corporation I350 Ethernet Controller Virtual Function (rev 01)
04:00.0 Ethernet controller: Realtek Semiconductor Co., Ltd. RTL8111/8168/8411 PCI Express Gigabit Ethernet Controller (rev 15)
Check if ACS is supported.
sudo lspci -vv | grep "Access Control Services" -C 5
...
Kernel driver in use: pcieport
00:1d.0 PCI bridge: Intel Corporation 200 Series PCH PCI Express Root Port #11 (rev f0) (prog-if 00 [Normal decode])
--
Device specific mode supported
Steering table in TPH capability structure
Capabilities: [1c0 v1] Latency Tolerance Reporting
Max snoop latency: 71680ns
Max no snoop latency: 71680ns
Capabilities: [1d0 v1] Access Control Services
ACSCap: SrcValid- TransBlk- ReqRedir- CmpltRedir- UpstreamFwd- EgressCtrl- DirectTrans-
ACSCtl: SrcValid- TransBlk- ReqRedir- CmpltRedir- UpstreamFwd- EgressCtrl- DirectTrans-
Kernel driver in use: igb
Kernel modules: igb
--
Region 3: Memory at 00000000c8060000 (64-bit, prefetchable)
VF Migration: offset: 00000000, BIR: 0
Capabilities: [1a0 v1] Transaction Processing Hints
...
Capabilities: [1d0 v1] Access Control Services
ACSCap: SrcValid- TransBlk- ReqRedir- CmpltRedir- UpstreamFwd- EgressCtrl- DirectTrans-
ACSCtl: SrcValid- TransBlk- ReqRedir- CmpltRedir- UpstreamFwd- EgressCtrl- DirectTrans-
ACSCap is the ACS Capability, +/- indicates supported/not supported.
ACSCtl is the ACS capability that is enabled, +/- indicates enabled/disabled.
ACS Override Patch
Install linux-vfio and overwrite ACS.
paru -S linux-vfio
Add kernel options and update the grub configuration.
sudo vim /etc/default/grub
-GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX_DEFAULT="loglevel=3 quiet intel_iommu=on iommu=pt pci=assign-busses"
+GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX_DEFAULT="loglevel=3 quiet intel_iommu=on iommu=pt pci=assign-busses pcie_acs_override=downstream"
sudo grub-mkconfig -o /boot/grub/grub.cfg
reboot
Create VMs
Create a VM in Virtual Machine Manager.
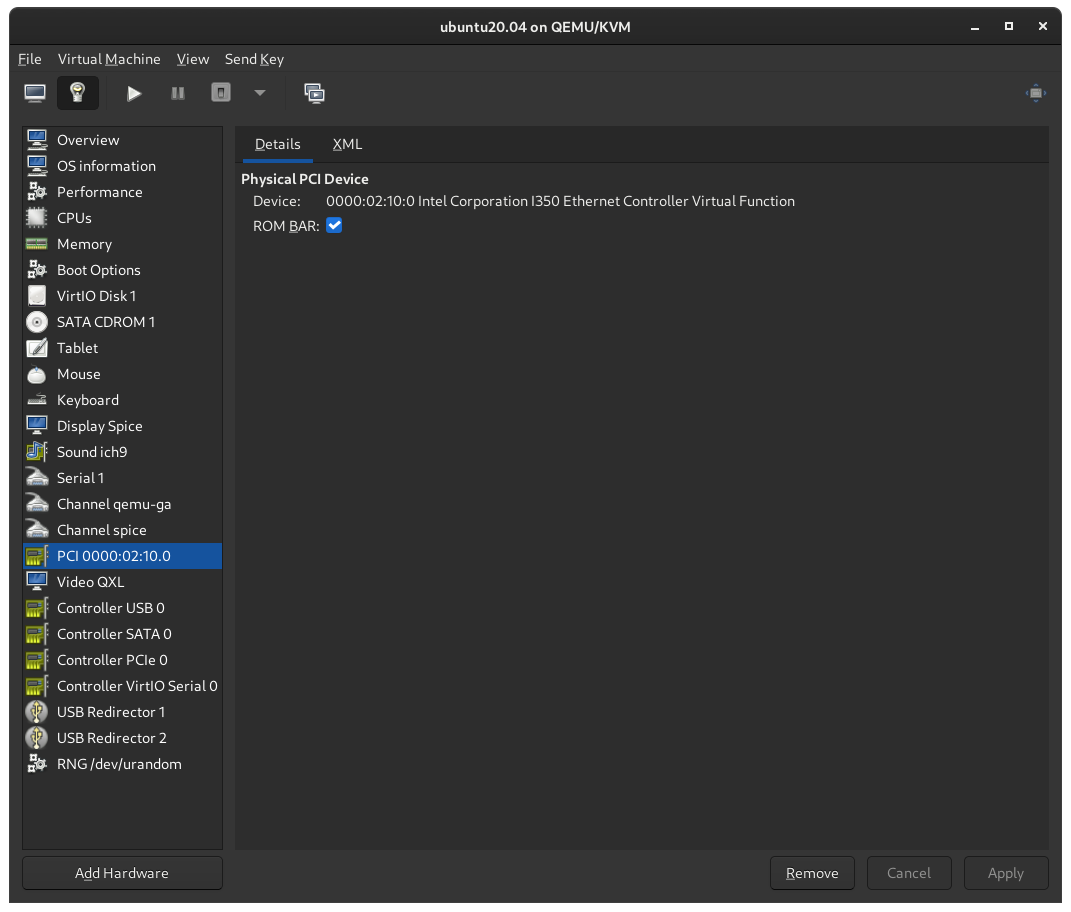
IP info
The network information before and after starting the VM is as follows.
- Before:
ip a | grep enp1s
3: enp1s0f0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc mq state UP group default qlen 1000
inet 192.168.0.170/24 brd 192.168.0.255 scope global dynamic noprefixroute enp1s0f0
4: enp1s0f1: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc mq state UP group default qlen 1000
inet 192.168.0.171/24 brd 192.168.0.255 scope global dynamic noprefixroute enp1s0f1
6: enp1s0f0v1: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc fq_codel state UP group default qlen 1000
inet 192.168.0.110/24 brd 192.168.0.255 scope global dynamic noprefixroute enp1s0f0v1
7: enp1s0f0v2: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc fq_codel state UP group default qlen 1000
inet 192.168.0.111/24 brd 192.168.0.255 scope global dynamic noprefixroute enp1s0f0v2
8: enp1s0f0v3: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc fq_codel state UP group default qlen 1000
inet 192.168.0.212/24 brd 192.168.0.255 scope global dynamic noprefixroute enp1s0f0v3
10: enp1s0f1v1: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc fq_codel state UP group default qlen 1000
inet 192.168.0.197/24 brd 192.168.0.255 scope global dynamic noprefixroute enp1s0f1v1
11: enp1s0f1v2: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc fq_codel state UP group default qlen 1000
inet 192.168.0.191/24 brd 192.168.0.255 scope global dynamic noprefixroute enp1s0f1v2
12: enp1s0f1v3: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc fq_codel state UP group default qlen 1000
inet 192.168.0.117/24 brd 192.168.0.255 scope global dynamic noprefixroute enp1s0f1v3
19: enp1s0f0v0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc fq_codel state UP group default qlen 1000
inet 192.168.0.199/24 brd 192.168.0.255 scope global dynamic noprefixroute enp1s0f0v0
20: enp1s0f1v0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc fq_codel state UP group default qlen 1000
inet 192.168.0.136/24 brd 192.168.0.255 scope global dynamic noprefixroute enp1s0f1v0
- After:
ip a | grep enp1s
3: enp1s0f0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc mq state UP group default qlen 1000
inet 192.168.0.170/24 brd 192.168.0.255 scope global dynamic noprefixroute enp1s0f0
4: enp1s0f1: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc mq state UP group default qlen 1000
inet 192.168.0.171/24 brd 192.168.0.255 scope global dynamic noprefixroute enp1s0f1
6: enp1s0f0v1: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc fq_codel state UP group default qlen 1000
inet 192.168.0.110/24 brd 192.168.0.255 scope global dynamic noprefixroute enp1s0f0v1
7: enp1s0f0v2: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc fq_codel state UP group default qlen 1000
inet 192.168.0.111/24 brd 192.168.0.255 scope global dynamic noprefixroute enp1s0f0v2
8: enp1s0f0v3: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc fq_codel state UP group default qlen 1000
inet 192.168.0.212/24 brd 192.168.0.255 scope global dynamic noprefixroute enp1s0f0v3
10: enp1s0f1v1: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc fq_codel state UP group default qlen 1000
inet 192.168.0.197/24 brd 192.168.0.255 scope global dynamic noprefixroute enp1s0f1v1
11: enp1s0f1v2: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc fq_codel state UP group default qlen 1000
inet 192.168.0.191/24 brd 192.168.0.255 scope global dynamic noprefixroute enp1s0f1v2
12: enp1s0f1v3: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc fq_codel state UP group default qlen 1000
inet 192.168.0.117/24 brd 192.168.0.255 scope global dynamic noprefixroute enp1s0f1v3
Speedtest
I ran a speed test on the host and VM to check the speed. I was expecting to get near-native speed with SR-IOV, but the overhead was unexpectedly large.
- Host
mori@arch-server ~ % speedtest-cli --server 15047
Retrieving speedtest.net configuration...
Testing from NTT (122.24.178.237)...
Retrieving speedtest.net server list...
Retrieving information for the selected server...
Hosted by OPEN Project (via 20G SINET) (Tokyo) [1.82 km]: 50.513 ms
Testing download speed................................................................................
Download: 83.80 Mbit/s
Testing upload speed......................................................................................................
Upload: 98.05 Mbit/s
- VM1
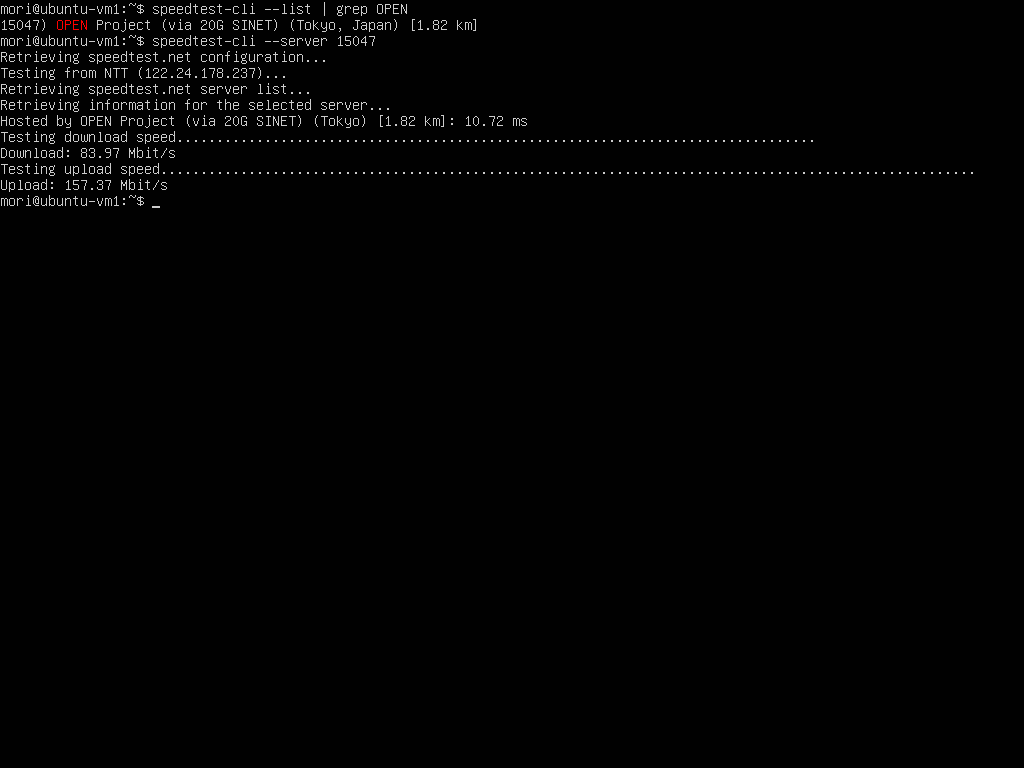
- VM2
References
https://downloadmirror.intel.com/13663/eng/readme_5.5.2.txt
https://qiita.com/m10i/items/980a350f898f28eac613
https://metonymical.hatenablog.com/entry/2018/04/11/193408
https://github.com/k8snetworkplumbingwg/sriov-network-device-plugin/blob/master/docs/vf-setup.md
https://www.heiko-sieger.info/iommu-groups-what-you-need-to-consider/