Dual boot (with Windows 10) + btrfs + grub
Install Arch Linux with the following settings.
| Settings | |
|---|---|
| Dual Booting | Windows 10 |
| Filesystem | Btrfs |
| Boot Loader | GRUB |
| Disk | single-disk |
| Disk Encryption | false |
Install Windows 10
diskpart
At first, install Windows 10.
Boot from ISO which can be downloaded from here, and choose drive to install Windows 10.
You can install with the default layout, but I recommend to use custom layout. This is because the size of the default EFI partition is 100 MB.
It is possible to manage linux and windows images in that size of partition, but some tweaks is needed, for example, compressing initramfs with xz.
In this example I will allocate 500 MB for the EFI partition.
When the following installation screen appears, press shift + F10 to open cmd.
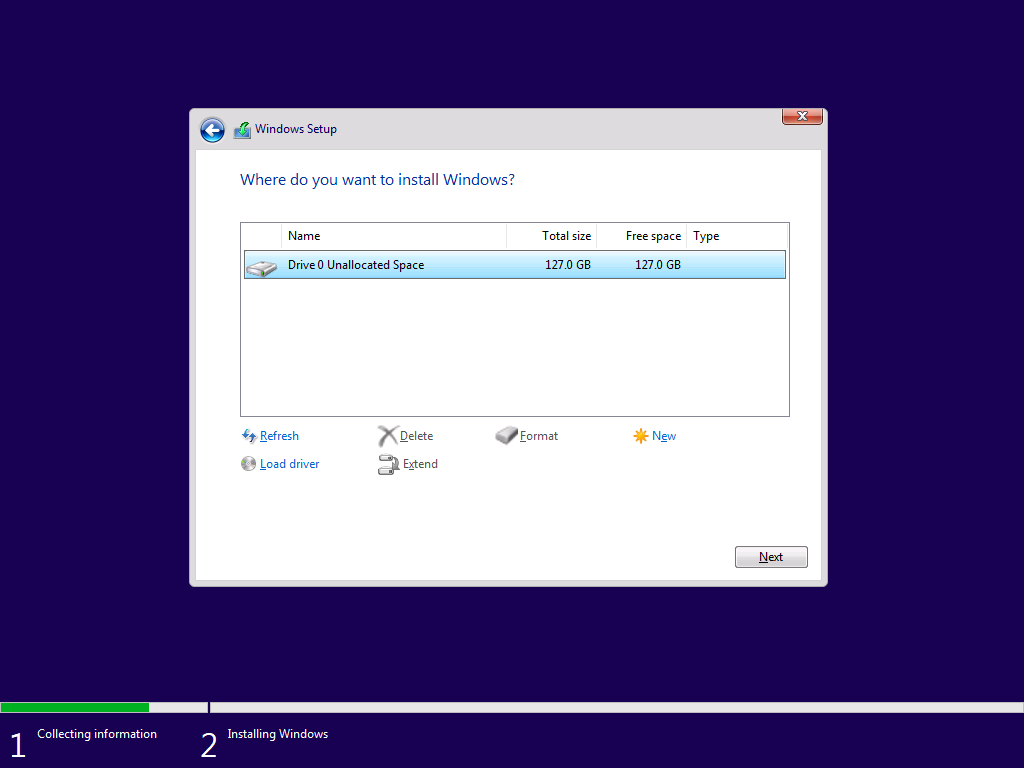
Then, use diskpart for partitioning.
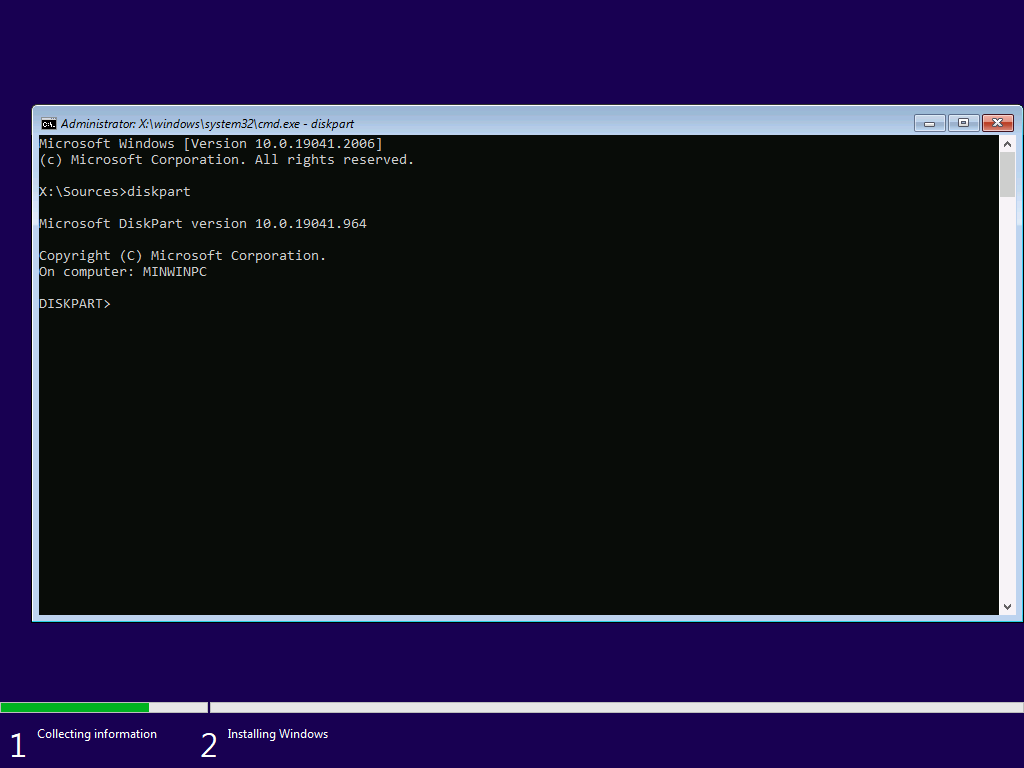
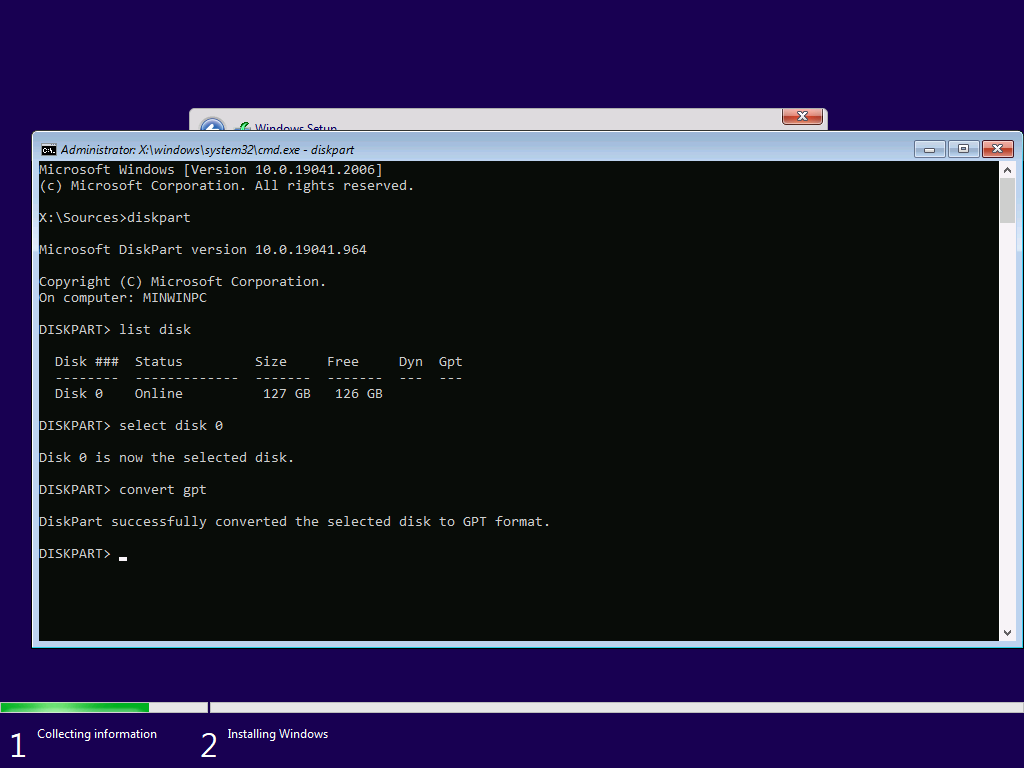
Select a disk with SELECT and convert it to GPT if necessary.
CREATE to create partitions.
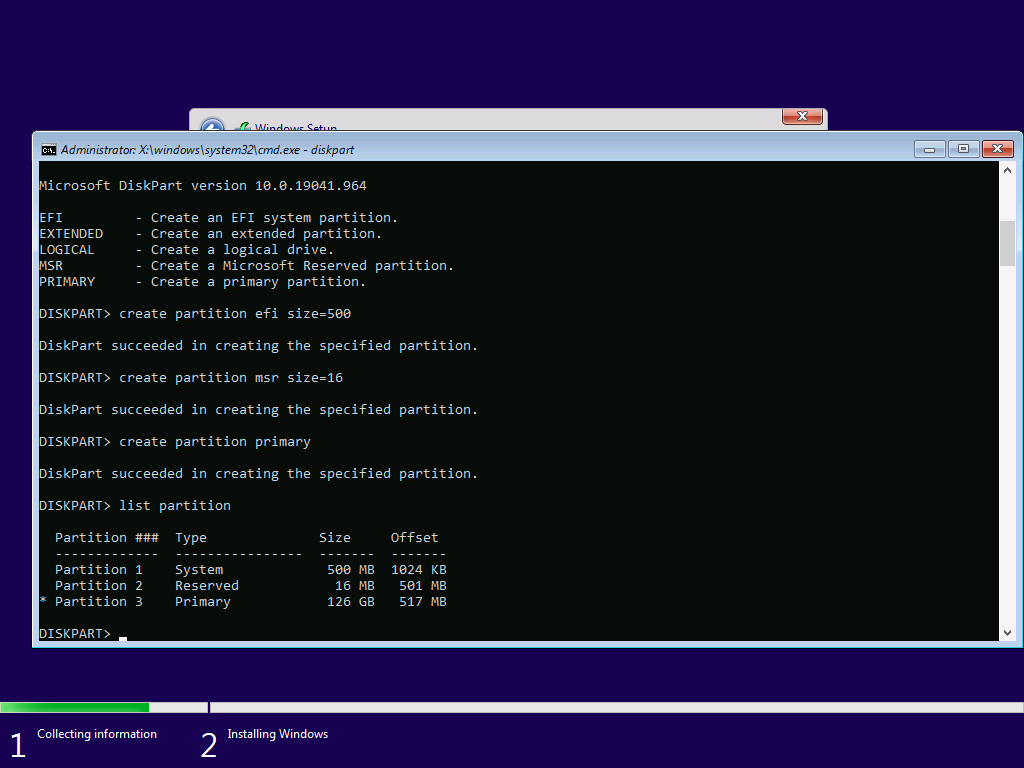
Each command is explained by running help, so if you do not understand a command, you can look it up as needed.
After partitioning, exit diskpart and cmd.
Press Refresh and install Windows 10 on the primary partition.
Bypass sign-in (option)
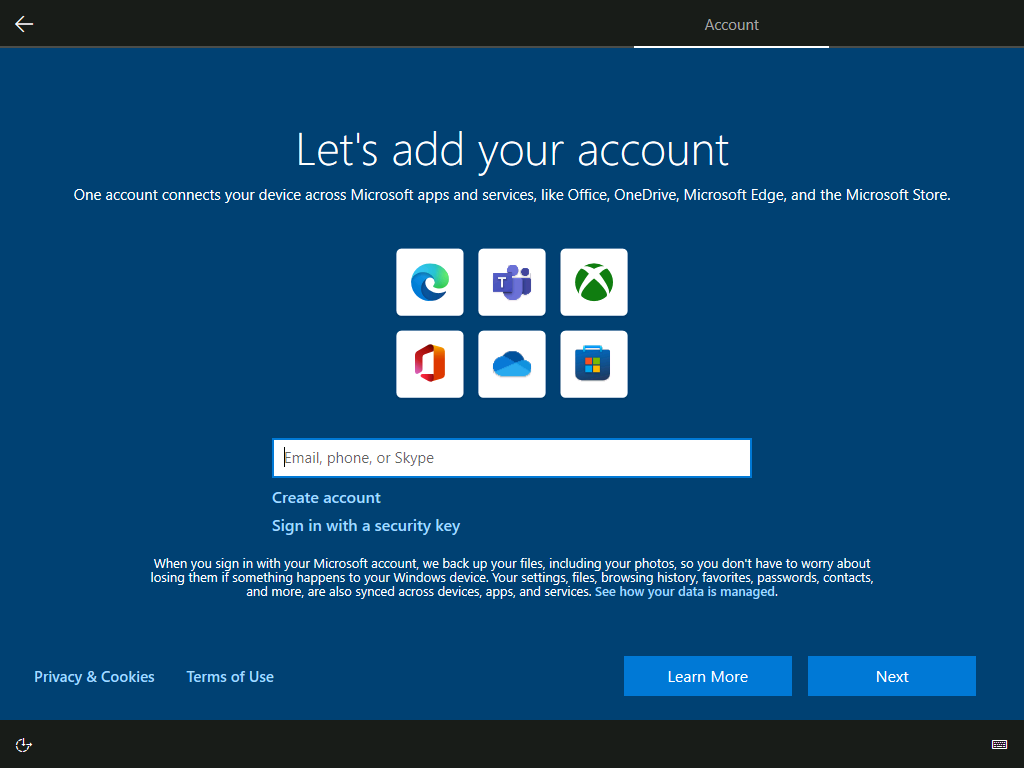
When you see sign-in window like above, press Shift + F10 and run:
ipconfig release
It will turn off the network so that sign-in fails and you can install with a local account.
Shrink
We need to get a free disk for Linux, so we start the disk manager and shrink the disk.
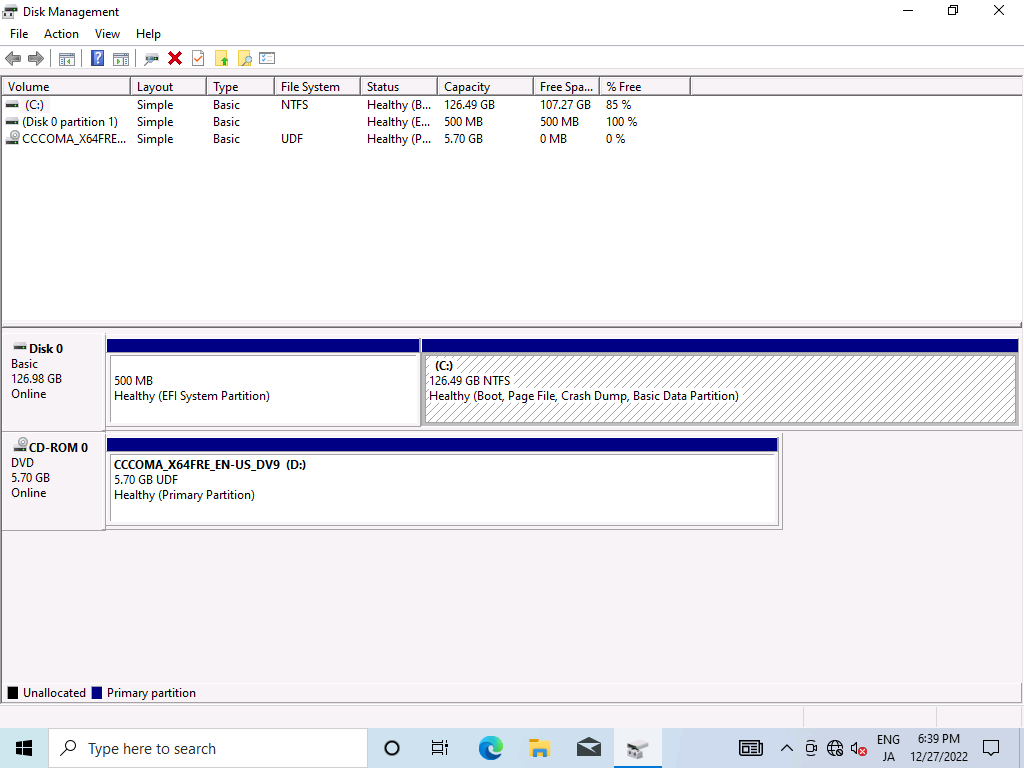
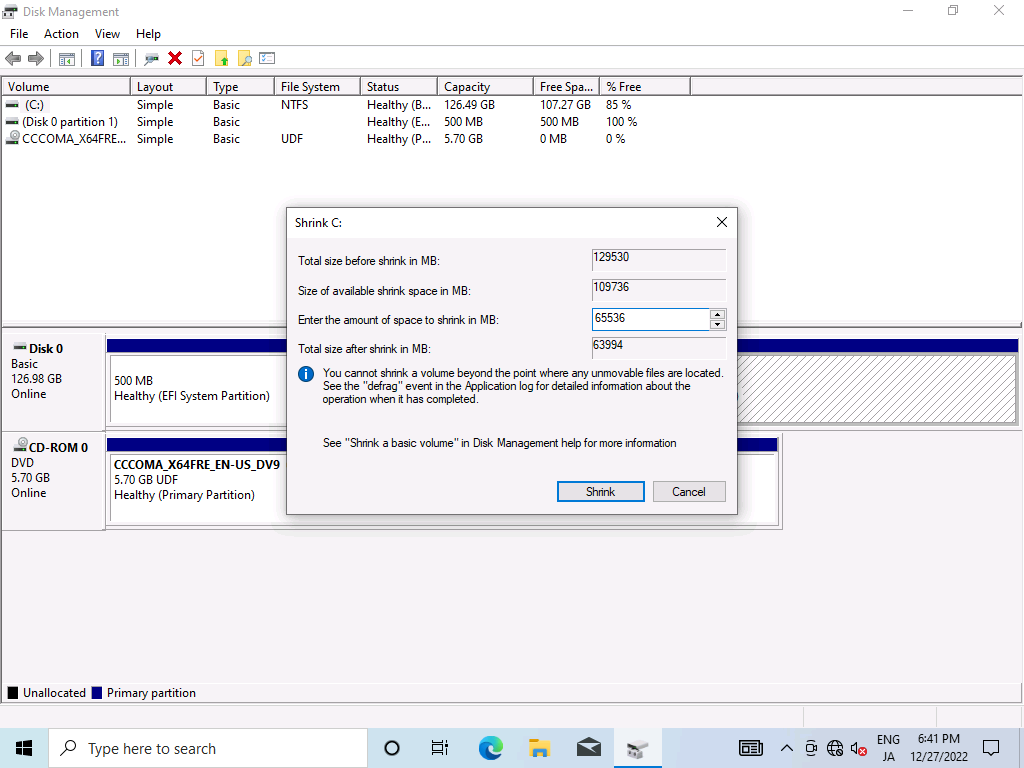
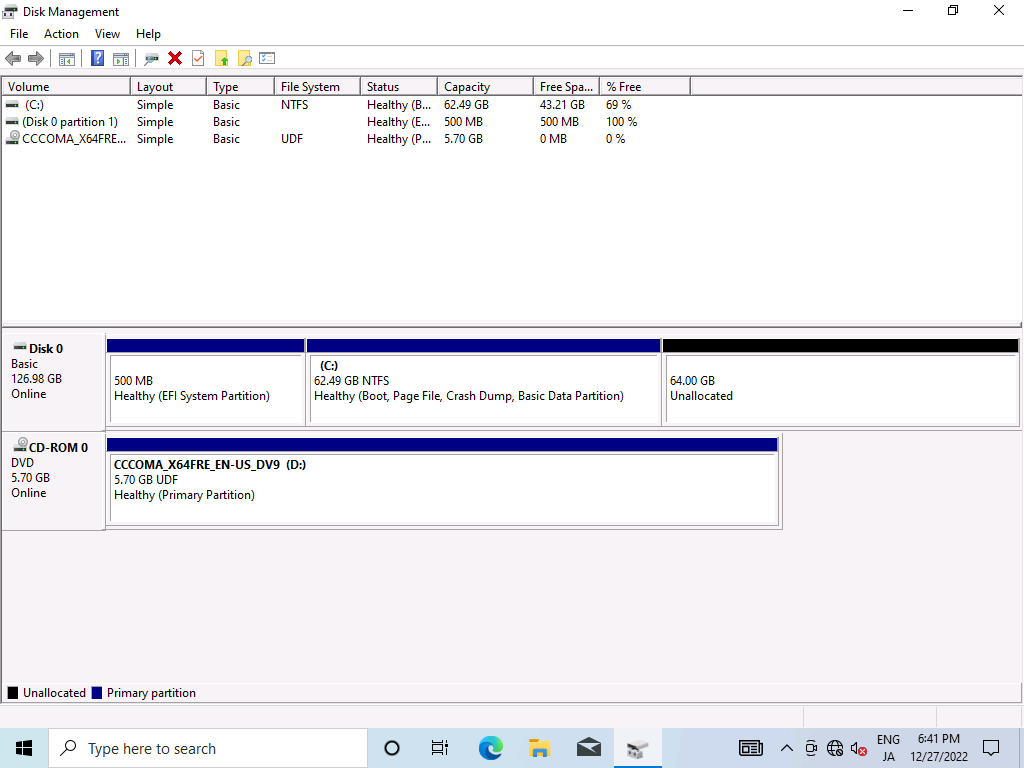
After that, downloads Arch Linux ISO from here and boot.
Install Arch Linux
Change Keymaps
Change the keymap to the one you use for the installation. For a Japanese keyboard, use jp106.
loadkeys jp106
Time Settings
Execute the following command to use the NTP (Network Time Protocol).
timedatectl set-ntp true
Optimizing Mirrorlist
Optimize the mirror list using reflector to access mirror servers with fast access during installation.
pacman -Syy
pacman -S reflector # `python` might be required
reflector -c Japan --sort rate -a 6 --save /etc/pacman.d/mirrorlist
The meaning of the reflector option is as follows.
| Options | Description |
|---|---|
-c Japan | Restrict mirrors to selected countries. |
--sort rate | Sort by download rate. |
-a 6 | Restrict to servers synchronized within 6 hours. |
--save /etc/pacman.d/mirrorlist | Save the mirror list to the specified path. |
Disk Partitioning and Formatting
We will assume that the partition in /dev/sda is as follows.
sda
├─sda1 <-- EFI Partition
├─sda2 <-- MSR
├─sda3 <-- Windows
└─sda4 <-- Empty Partition for Linux
First, update the partition table so that the empty partition you created is used as Linux Filesystem.
gdisk /dev/sda
Format the Linux filesystem partition with BTRFS, create a subvolume, and mount it.
mkfs.btrfs /dev/sda4
mount /dev/sda4 /mnt
btrfs su cr /mnt/@
btrfs su cr /mnt/@home
btrfs su cr /mnt/@snapshots
btrfs su cr /mnt/@var_log
umount /mnt
mount -o noatime,compress=zstd,space_cache=v2,subvol=@ /dev/sda4 /mnt
mkdir -p /mnt/{boot,home,.snapshots,var/log}
mount -o noatime,compress=zstd,space_cache=v2,subvol=@home /dev/sda4 /mnt/home
mount -o noatime,compress=zstd,space_cache=v2,subvol=@snapshots /dev/sda4 /mnt/.snapshots
mount -o noatime,compress=zstd,space_cache=v2,subvol=@var_log /dev/sda4 /mnt/var/log
mount /dev/sda4 /mnt/boot
Base install
Install the package in the root directory, /mnt.
- Intel
- AMD
pacstrap /mnt base linux linux-firmware vim intel-ucode
pacstrap /mnt base linux linux-firmware vim amd-ucode
fstab
Generate the fstab file, which holds the information about which device to mount.
genfstab -U /mnt >> /mnt/etc/fstab
Change the Root Directory
Use chroot to set /mnt as the root directory.
arch-chroot /mnt
Localization
Create a symbolic link to /etc/localtime to change the time zone.
ln -sf /usr/share/zoneinfo/Asia/Tokyo /etc/localtime
Set the hardware clock to the current system clock. The system clock is the clock managed by the OS, and the hardware clock is the clock managed by the motherboard (hardware). when the OS is rebooted, the system clock stored in memory is lost, so the time is obtained from the hardware clock.
hwclock --systohc
To set the locale, first generate the locale. Uncomment the entries you want to use in /etc/locale.gen and run locale-gen.
vim /etc/locale.gen
- # en_US.UTF-8 UTF-8
+ en_US.UTF-8 UTF-8
locale-gen
Execute the following command to set the locale of the system.
echo LANG=en_US.UTF-8 >> /etc/locale.conf
echo KEYMAP=jp106 >> /etc/vconsole.conf
Hostname
Register hostname in /etc/hostname.
vim /etc/hostname
+ arch
Edit /etc/hosts and set IP address corresponding to hostname.
vim /etc/hosts
+ 127.0.0.1 localhost
+ ::1 localhost
+ 127.0.1.1 arch.localdomain arch
Root Password
Set the password of root user.
passwd
Install Additional Packages
pacman -S grub efibootmgr networkmanager network-manager-applet \
dialog os-prober mtools dosfstools base-devel linux-headers snapper \
reflector cron git xdg-utils xdg-user-dirs ntfs-3g
Configuring mkinitcpio
Change the configurations, and reflect the changes with mkinitcpio.
vim /etc/mkinitcpio.conf
- MODULES=()
+ MODULES=(btrfs)
mkinitcpio -p linux
Bootloader
Install Grub and create config file.
grub-install --target=x86_64-efi --efi-directory=/boot --bootloader-id=GRUB
grub-mkconfig -o /boot/grub/grub.cfg
Systemd
Enables NetworkManager.
systemctl enable NetworkManager
Enables Bluetooth.
systemctl enable bluetooth
Enables reflector. The execution options are written in /etc/xdg/reflector/reflector.conf.
systemctl enable reflector.service # update mirrorlist every boot
systemctl enable reflector.timer # update mirrorlist weekly
Add User
Add user with useradd and set the password.
useradd -mG wheel mori
passwd mori
Give the user priviledges.
EDITOR=vim visudo
- # %wheel ALL=(ALL) ALL
+ %wheel ALL=(ALL) ALL
Reboot
exit
umount -a
reboot
Trouble shooting
- Boot entry for windows disappears from grub boot loader
- Add
GRUB_DISABLE_OS_PROBER=falseto/etc/default/gruband recreate grub.cfg - The problem is deactivated os-prober. os-prober automatically finds operating systems and adds their boot entry, but sometimes it is deactivated. The option reactivate os-prober.
- Add